| Classification |
Composition characteristics |
Microscopic microstructure |
Performance features |
Typical alloy |
| α-type Titanium alloy |
All α-type Titanium alloys |
Contains less than 6% Aluminum and a small amount of neutral elements |
After annealing, except for a small amount of β phase caused by impurity elements, almost all α phase |
Low density, good thermal strength, good weldability, good ultra-low temperature toughness |
TA5~TA7 TA7EL |
| Near-α type Titanium alloy |
In addition to Aluminum and neutral elements, there are small amounts (no more than 4%) of stable elements |
In addition to a large amount of phase α after annealing, there is a small amount (about 10%, volume fraction) of the β phase |
It can be strengthened by heat treatment, has good thermal strength and thermal stability, and has good weldability |
Ti75~TA12 |
| α+ compound type Titanium alloy |
A small amount of active eutectoid element is added on the basis of all α type titanium alloy |
In addition to a large amount of α phase, there are a small amount of β phase and intermetallic compounds after annealing |
It has precipitation hardening effect, improves tensile strength and creep strength at room temperature and high temperature, and has good weldability |
TA8 |
| β-type Titanium alloy |
Contains a certain amount of aluminum and different content of β stable elements and neutral elements |
After annealing, there are different proportions of α phase and β phase |
Heat treatment can be strengthened, strength and hardenability with the increase of β stable elements and improve weldability is better, general cold forming and cold working ability is poor,TC4ELI alloy has good ultra-low temperature toughness,TC4ELI alloy processed by β has good damage tolerance performance |
TC3~C12 TC4ELI |
| β-type Titanium alloy |
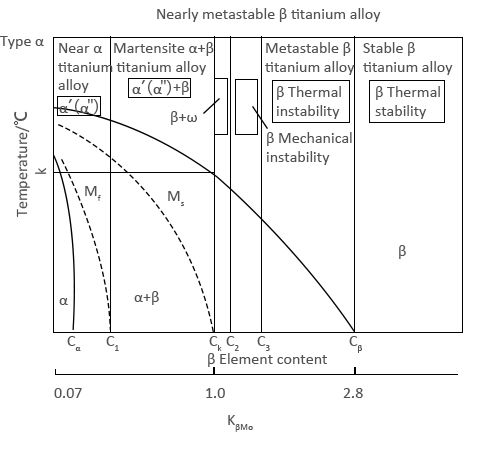
Heat stable β Titanium alloy |
Contains large amounts of β stable elements and sometimes small amounts of other elements |
After annealing, all are β phase |
Low strength at room temperature, strong cold forming and cold processing ability, good corrosion resistance in reducing media, thermal stability, good weldability |
TB7 |
| Metastable β Titanium alloy |
Contains large critical concentrations of more than a small amount of β-stable elements of aluminum (generally not more than 3%) and neutral elements |
After solid solution treatment (water quenching or air cooling) from β phase region, almost all of them are metastable β phase. During aging, α phase is precipitated in β phase, after aging, there are β phase and α phase |
After solution treatment, the temperature strength is low, the cold forming and cold working ability is strong, and the weldability is good. After aging, the alloy has high strength at room temperature, high fracture toughness at high yield strength, poor thermal stability above 350℃, and good quenching type |
TB1~B5、TB8 TB9 |
| Near-β Titanium alloy |
Contains about a critical concentration of β stable elements and a certain amount of neutral elements and aluminum |
There is a large amount of metastable β phase after solid solution treatment from β phase region, and a small amount of other metastable phases (α' or ω phase) after aging to β phase and α phase region solid solution treatment, WO or AC. After aging, the fracture toughness and plasticity are higher at high strength, while α+β phase solution treatment and FC at medium strength can obtain high fracture toughness and plasticity |
In addition to the characteristics of metastable β-type titanium alloys, β-phase solid solution treatment has low yield strength and high uniform elongation. |
TB6、TB10 |